Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
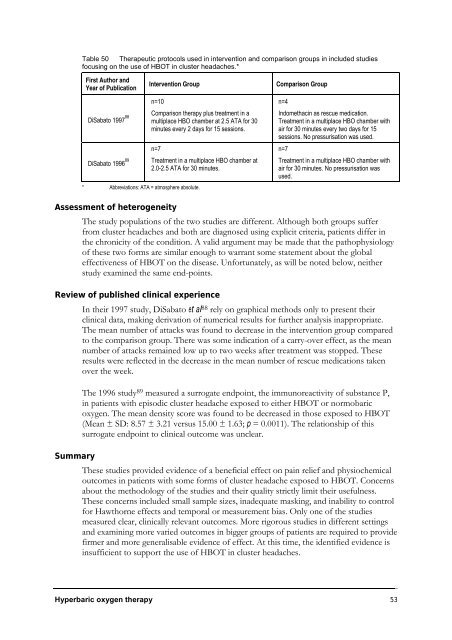
Table 50 Therapeutic protocols used in intervention and comparison groups in included studies<br />
focusing on the use of HBOT in cluster headaches.*<br />
First Author and<br />
Year of Publication<br />
DiSabato 1997 88<br />
DiSabato 1996 89<br />
* Abbreviations: ATA = atmosphere absolute.<br />
Intervention Group Comparison Group<br />
n=10<br />
Comparison therapy plus treatment in a<br />
multiplace HBO chamber at 2.5 ATA for 30<br />
minutes every 2 days for 15 sessions.<br />
n=7<br />
Treatment in a multiplace HBO chamber at<br />
2.0-2.5 ATA for 30 minutes.<br />
n=4<br />
Indomethacin as rescue medication.<br />
Treatment in a multiplace HBO chamber with<br />
air for 30 minutes every two days for 15<br />
sessions. No pressurisation was used.<br />
n=7<br />
Treatment in a multiplace HBO chamber with<br />
air for 30 minutes. No pressurisation was<br />
used.<br />
Assessment of heterogeneity<br />
The study populations of the two studies are different. Although both groups suffer<br />
from cluster headaches and both are diagnosed using explicit criteria, patients differ in<br />
the chronicity of the condition. A valid argument may be made that the pathophysiology<br />
of these two forms are similar enough to warrant some statement about the global<br />
effectiveness of HBOT on the disease. Unfortunately, as will be noted below, neither<br />
study examined the same end-points.<br />
Review of published clinical experience<br />
In their 1997 study, DiSabato et al88 rely on graphical methods only to present their<br />
clinical data, making derivation of numerical results for further analysis inappropriate.<br />
The mean number of attacks was found to decrease in the intervention group compared<br />
to the comparison group. There was some indication of a carry-over effect, as the mean<br />
number of attacks remained low up to two weeks after treatment was stopped. These<br />
results were reflected in the decrease in the mean number of rescue medications taken<br />
over the week.<br />
The 1996 study 89 measured a surrogate endpoint, the immunoreactivity of substance P,<br />
in patients with episodic cluster headache exposed to either HBOT or normobaric<br />
oxygen. The mean density score was found to be decreased in those exposed to HBOT<br />
(Mean ± SD: 8.57 ± 3.21 versus 15.00 ± 1.63; p = 0.0011). The relationship of this<br />
surrogate endpoint to clinical outcome was unclear.<br />
Summary<br />
These studies provided evidence of a beneficial effect on pain relief and physiochemical<br />
outcomes in patients with some forms of cluster headache exposed to HBOT. Concerns<br />
about the methodology of the studies and their quality strictly limit their usefulness.<br />
These concerns included small sample sizes, inadequate masking, and inability to control<br />
for Hawthorne effects and temporal or measurement bias. Only one of the studies<br />
measured clear, clinically relevant outcomes. More rigorous studies in different settings<br />
and examining more varied outcomes in bigger groups of patients are required to provide<br />
firmer and more generalisable evidence of effect. At this time, the identified evidence is<br />
insufficient to support the use of HBOT in cluster headaches.<br />
<strong>Hyperbaric</strong> oxygen therapy 53