Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
outcomes or that decreased the risk of harmful end-points will tend to make groups<br />
more similar to each other when these outcomes are eventually compared.<br />
If the assumption is made that the technology used in the delivery of hyperbaric oxygen<br />
was similar in the two studies, then the intervention protocols used by the two research<br />
groups differ only in the dose used. However, this difference is by a factor of 16. In the<br />
study by Stavitsky et al, 77 patients were exposed to HBO at 2 ATA for 2 hours. Thurston<br />
et al 78 reports exposure to HBO at the same pressure, but prescribed for 16 continuous<br />
three-hour cycles (2/3 under pressure).<br />
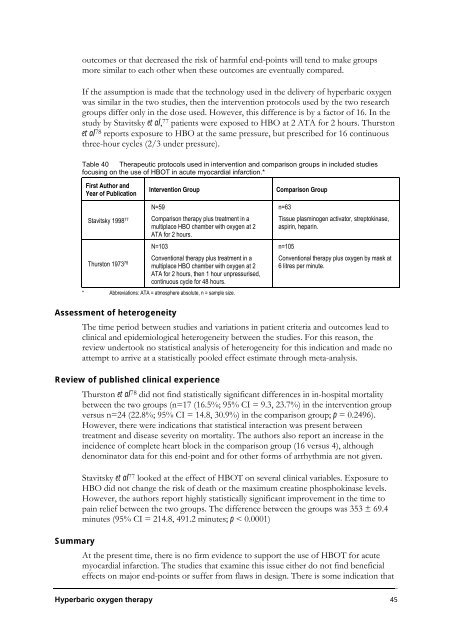
Table 40 Therapeutic protocols used in intervention and comparison groups in included studies<br />
focusing on the use of HBOT in acute myocardial infarction.*<br />
First Author and<br />
Year of Publication<br />
Stavitsky 1998 77<br />
Thurston 1973 78<br />
Intervention Group Comparison Group<br />
N=59<br />
Comparison therapy plus treatment in a<br />
multiplace HBO chamber with oxygen at 2<br />
ATA for 2 hours.<br />
N=103<br />
Conventional therapy plus treatment in a<br />
multiplace HBO chamber with oxygen at 2<br />
ATA for 2 hours, then 1 hour unpressurised,<br />
continuous cycle for 48 hours.<br />
* Abbreviations: ATA = atmosphere absolute, n = sample size.<br />
n=63<br />
Tissue plasminogen activator, streptokinase,<br />
aspirin, heparin.<br />
n=105<br />
Conventional therapy plus oxygen by mask at<br />
6 litres per minute.<br />
Assessment of heterogeneity<br />
The time period between studies and variations in patient criteria and outcomes lead to<br />
clinical and epidemiological heterogeneity between the studies. For this reason, the<br />
review undertook no statistical analysis of heterogeneity for this indication and made no<br />
attempt to arrive at a statistically pooled effect estimate through meta-analysis.<br />
Review of published clinical experience<br />
Thurston et al78 did not find statistically significant differences in in-hospital mortality<br />
between the two groups (n=17 (16.5%; 95% CI = 9.3, 23.7%) in the intervention group<br />
versus n=24 (22.8%; 95% CI = 14.8, 30.9%) in the comparison group; p = 0.2496).<br />
However, there were indications that statistical interaction was present between<br />
treatment and disease severity on mortality. The authors also report an increase in the<br />
incidence of complete heart block in the comparison group (16 versus 4), although<br />
denominator data for this end-point and for other forms of arrhythmia are not given.<br />
Stavitsky et al 77 looked at the effect of HBOT on several clinical variables. Exposure to<br />
HBO did not change the risk of death or the maximum creatine phosphokinase levels.<br />
However, the authors report highly statistically significant improvement in the time to<br />
pain relief between the two groups. The difference between the groups was 353 ± 69.4<br />
minutes (95% CI = 214.8, 491.2 minutes; p < 0.0001)<br />
Summary<br />
At the present time, there is no firm evidence to support the use of HBOT for acute<br />
myocardial infarction. The studies that examine this issue either do not find beneficial<br />
effects on major end-points or suffer from flaws in design. There is some indication that<br />
<strong>Hyperbaric</strong> oxygen therapy 45