Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
characteristics compared to the treatment group, which may be predictive of outcome<br />
independent of allocation.<br />
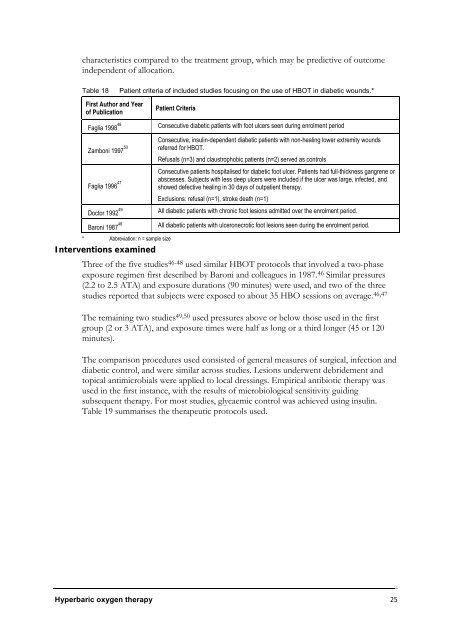
Table 18 Patient criteria of included studies focusing on the use of HBOT in diabetic wounds.*<br />
First Author and Year<br />
of Publication<br />
Patient Criteria<br />
Faglia 1998 48 Consecutive diabetic patients with foot ulcers seen during enrolment period<br />
Zamboni 1997 50<br />
Consecutive, insulin-dependent diabetic patients with non-healing lower extremity wounds<br />
referred for HBOT.<br />
Refusals (n=3) and claustrophobic patients (n=2) served as controls<br />
Faglia 1996 47<br />
Consecutive patients hospitalised for diabetic foot ulcer. Patients had full-thickness gangrene or<br />
abscesses. Subjects with less deep ulcers were included if the ulcer was large, infected, and<br />
showed defective healing in 30 days of outpatient therapy.<br />
Exclusions: refusal (n=1), stroke death (n=1)<br />
Doctor 1992 49 All diabetic patients with chronic foot lesions admitted over the enrolment period.<br />
Baroni 1987 46 All diabetic patients with ulceronecrotic foot lesions seen during the enrolment period.<br />
* Abbreviation: n = sample size<br />
Interventions examined<br />
Three of the five studies46-48 used similar HBOT protocols that involved a two-phase<br />
exposure regimen first described by Baroni and colleagues in 1987. 46 Similar pressures<br />
(2.2 to 2.5 ATA) and exposure durations (90 minutes) were used, and two of the three<br />
studies reported that subjects were exposed to about 35 HBO sessions on average. 46,47<br />
The remaining two studies 49,50 used pressures above or below those used in the first<br />
group (2 or 3 ATA), and exposure times were half as long or a third longer (45 or 120<br />
minutes).<br />
The comparison procedures used consisted of general measures of surgical, infection and<br />
diabetic control, and were similar across studies. Lesions underwent debridement and<br />
topical antimicrobials were applied to local dressings. Empirical antibiotic therapy was<br />
used in the first instance, with the results of microbiological sensitivity guiding<br />
subsequent therapy. For most studies, glycaemic control was achieved using insulin.<br />
Table 19 summarises the therapeutic protocols used.<br />
<strong>Hyperbaric</strong> oxygen therapy 25