Income, Poverty, and Health Insurance Coverage ... - Census Bureau
Income, Poverty, and Health Insurance Coverage ... - Census Bureau
Income, Poverty, and Health Insurance Coverage ... - Census Bureau
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
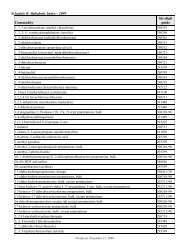
Table 2.<br />
Change in Real Median <strong>Income</strong> <strong>and</strong> Earnings, Number of Workers, <strong>and</strong> Percentage of Full-Time,<br />
Year-Round Workers During <strong>Income</strong> Years Surrounding Recessions by Sex: 1969 to 2009<br />
(<strong>Income</strong> <strong>and</strong> earnings in 2009 dollars Information for people 15 years <strong>and</strong> older beginning with 1980 <strong>and</strong> people 14 years <strong>and</strong> older for previous years<br />
Before 1989, earnings are for civilian workers only For information on confidentiality protection, sampling error, nonsampling error, <strong>and</strong> definitions, see<br />
www.census.gov/apsd/techdoc/cps/cpsmar10.pdf)<br />
Recessions 1<br />
<strong>Income</strong><br />
years<br />
Per-<br />
centage<br />
change<br />
in real<br />
median<br />
household<br />
income<br />
Change in<br />
number of<br />
workers with<br />
earnings<br />
(in thous<strong>and</strong>s)<br />
Change in<br />
number of<br />
full-time, yearround<br />
workers<br />
with earnings<br />
(in thous<strong>and</strong>s)<br />
Percentagepoint<br />
change in<br />
the percentage<br />
of full-time,<br />
year-round<br />
workers<br />
with earnings<br />
Percentage<br />
change in<br />
median<br />
earnings of<br />
all workers<br />
Percentage<br />
change in<br />
median<br />
earnings of<br />
full-time, yearround<br />
workers<br />
Male Female Male Female Male Female Male Female Male Female<br />
December 2007, trough not yet<br />
defined 2007 to 2009 *–42 *–2,548 *–1,323 *–6,931 *–2,396 *–61 *–22 *–41 *–28 *10 –01<br />
March 2001 to November 2001 1999 to 2002 * –35 * 1,178 358 462 * 1,005 –05 * 11 * –26 * 76 04 * 63<br />
July 1990 to March 1991 1989 to 1991<br />
January 1980 to July 1980 <strong>and</strong> July<br />
*–42 –5 458 *–1,790 *1,096 *–25 *14 *–60 10 –10 07<br />
1981 to November 1982 1978 to 1983 *–60 *2,235 *4,710 492 *4,252 *–15 *42 *–101 *64 *–56 10<br />
November 1973 to March 1975 1973 to 1975 *–57 –170 *1,343 *–2,314 257 *–37 –07 *–64 16 *–42 –05<br />
December 1969 to November 1970 1969 to 1971<br />
* Statistically significant at the 90 percent confidence level<br />
*–17 *1,613 *748 –189 *628 *–22 08 *–22 *63 *15 *26<br />
1 Recessions are determined by the National <strong>Bureau</strong> of Economic Research, a private research organization<br />
Note: <strong>Income</strong> years are based on peak income year prior to or during the start of the recession <strong>and</strong> the trough income year near or after the end of the recession<br />
Source: US <strong>Census</strong> <strong>Bureau</strong>, Current Population Survey, 1970 to 2010 Annual Social <strong>and</strong> Economic Supplements<br />
• Both men <strong>and</strong> women, 15 years old 2008 <strong>and</strong> 2009. 7 The changes for defined, the 4.2 percent income<br />
<strong>and</strong> over, who worked full-time, non-Hispanic Whites, Blacks, <strong>and</strong> decline is: 10<br />
year-round experienced increases<br />
in real median earnings between<br />
2008 <strong>and</strong> 2009. The median earn-<br />
ings of men increased 2.0 percent,<br />
from $46,191 to $47,127; <strong>and</strong><br />
the earnings of women increased<br />
Asians were not statistically signifi-<br />
8<br />
cant (Table 1).<br />
Household <strong>Income</strong><br />
Real median household income was<br />
$49,777 in 2009, not statistically<br />
• Not statistically different from the<br />
declines in income for the years surrounding<br />
the two recessions lasting<br />
from March 2001 to November 2001<br />
<strong>and</strong> from July 1990 to March 1991.<br />
by 1.9 percent, from $35,609 to different from the 2008 median. • Larger than the 1.7 percent decline<br />
$36,278. 6 In 2009, the female-to- Since 2007, the year before the most for the income years surrounding<br />
male earnings ratio was 0.77, not recent recession, median household the December 1969 to November<br />
statistically different from the 2008 income has declined 4.2 percent 1970 recession. 11<br />
•<br />
ratio (Table 1 <strong>and</strong> Figure 2).<br />
The median earnings of all working<br />
males 15 years old <strong>and</strong> over was<br />
(from $51,965) <strong>and</strong> is 5.0 percent<br />
below the median household income<br />
peak ($52,388) that occurred in 1999<br />
(Tables 1, 2, <strong>and</strong> A-1).<br />
• Smaller than the declines for the<br />
income years surrounding the<br />
January 1980 to July 1980 <strong>and</strong> July<br />
9 $36,331 in 2009, not statistically<br />
different from their 2008 median,<br />
while the earnings of their female<br />
Though the<br />
trough of the recession that began<br />
in December 2007 has not yet been<br />
1981 to November 1982 combined<br />
recessions (6.0 percent) <strong>and</strong> the<br />
November 1973 to March 1975<br />
counterparts increased by 1.9 recession (5.7 percent) (Figure 1<br />
percent, from $25,553 to $26,030 <strong>and</strong> Tables 1, 2, <strong>and</strong> A-1). 12<br />
(Table A-4).<br />
7 The difference between the declines for the<br />
overall <strong>and</strong> White populations was not statisti-<br />
• Real per capita income declined by<br />
cally significant.<br />
8 Unlike medians, per capita <strong>and</strong> means are<br />
10 Recessions are determined by the National<br />
<strong>Bureau</strong> of Economic Research, a private research<br />
1.2 percent for the total population,<br />
1.3 percent for Whites, <strong>and</strong><br />
affected by extremely high <strong>and</strong> low incomes.<br />
9 The difference between the percentage<br />
declines of 2007 to 2009 <strong>and</strong> 1999 to 2009 in<br />
organization. See Appendix A for a list of peak<br />
<strong>and</strong> trough months.<br />
11 Discussion is limited to recessions occurring<br />
3.5 percent for Hispanics between median household income was not statistically<br />
significant. In addition, the difference between<br />
after 1967, the first year that household income<br />
estimates were derived from the CPS ASEC.<br />
the 1999 <strong>and</strong> 2007 medians is not statistically<br />
12 The difference between the declines in<br />
6 The difference between the percentage<br />
increases in the earnings of men <strong>and</strong> women was<br />
not statistically significant.<br />
significant. The median household income peak<br />
of $52,388 in 1999 <strong>and</strong> the $52,301 median<br />
household income in 2000 are not statistically<br />
different.<br />
income for the combined January 1980 to July<br />
1980 <strong>and</strong> July 1981 to November 1982 reces-<br />
sions <strong>and</strong> the November 1973 to March 1975<br />
recession was not statistically significant.<br />
U.S. <strong>Census</strong> <strong>Bureau</strong> <strong>Income</strong>, <strong>Poverty</strong>, <strong>and</strong> <strong>Health</strong> <strong>Insurance</strong> <strong>Coverage</strong> in the United States: 2009 7