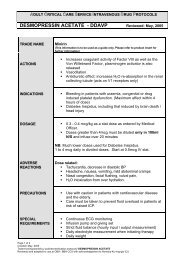
CRITICAL CARE
CRITICAL CARE
CRITICAL CARE
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Central Sydney Health Service Royal Prince Alfred Hospital<br />
ARTERIAL OXYGENATION GOAL<br />
Goal: SpO2 = 88 to 95 % or PaO2 = 55 to 80 mm Hg if ABG available<br />
� Adjust the FiO2 and PEEP according to the combinations outlined below. This can be<br />
performed every 5-10 minutes.<br />
� Adjustment to oxygenation can be made on SpO2 alone. It is not necessary to do blood<br />
gases to change FiO2. Blood gases should be performed as indicated. However, if a PaO2<br />
is available adjustments are made based on it, rather than SpO2.<br />
Fi02<br />
Peep<br />
0.3<br />
5<br />
0.4<br />
5<br />
0.4<br />
8<br />
0.5<br />
8<br />
0.5<br />
10<br />
0.6<br />
10<br />
ARTERIAL pH and PaCO2 / EtCO2<br />
Goal: pH = 7.30 – 7.45<br />
0.7<br />
� Leave the respiratory rate at the current settings<br />
Acidosis management: pH 7.10 – 7.30<br />
� Increase the ventilator rate until pH > 7.30 or PaCO2 < 35<br />
� PaCO2 is related to minute ventilation (MV = Vt x f)<br />
� Increasing f increases MV and “blows off” CO2 increasing pH<br />
� Maximum set ventilator rate is 35 bpm<br />
Acidosis Management: pH < 7.10<br />
� Increase the set ventilator rate to 35 bpm<br />
10<br />
� If pH remains < 7.10, tidal volume may be increased in 1ml/kg IBW steps until pH > 7.10<br />
Inform the senior register or duty consultant of an increase in tidal volume above 8 ml/kg<br />
IBW<br />
Alkalosis Management<br />
� Decrease the ventilator rate if possible<br />
0.7<br />
12<br />
0.7<br />
14<br />
0.8<br />
14<br />
0.9<br />
14<br />
0.9<br />
16<br />
0.9<br />
18<br />
1.0<br />
20-<br />
24