EFFECT OF VITAMINS C AND E INTAKE ON BLOOD ... - EuroJournals
EFFECT OF VITAMINS C AND E INTAKE ON BLOOD ... - EuroJournals
EFFECT OF VITAMINS C AND E INTAKE ON BLOOD ... - EuroJournals
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
European Journal of Social Sciences - Volume 2, Number 1 (2006)<br />
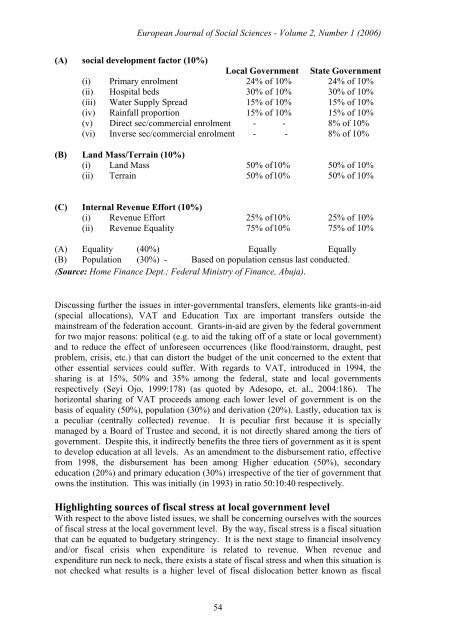
(A) social development factor (10%)<br />
Local Government State Government<br />
(i) Primary enrolment 24% of 10% 24% of 10%<br />
(ii) Hospital beds 30% of 10% 30% of 10%<br />
(iii) Water Supply Spread 15% of 10% 15% of 10%<br />
(iv) Rainfall proportion 15% of 10% 15% of 10%<br />
(v) Direct sec/commercial enrolment - - 8% of 10%<br />
(vi) Inverse sec/commercial enrolment - - 8% of 10%<br />
(B) Land Mass/Terrain (10%)<br />
(i) Land Mass 50% of 10% 50% of 10%<br />
(ii) Terrain 50% of 10% 50% of 10%<br />
(C) Internal Revenue Effort (10%)<br />
(i) Revenue Effort 25% of 10% 25% of 10%<br />
(ii) Revenue Equality 75% of 10% 75% of 10%<br />
(A) Equality (40%) Equally Equally<br />
(B) Population (30%) - Based on population census last conducted.<br />
(Source: Home Finance Dept.; Federal Ministry of Finance, Abuja).<br />
Discussing further the issues in inter-governmental transfers, elements like grants-in-aid<br />
(special allocations), VAT and Education Tax are important transfers outside the<br />
mainstream of the federation account. Grants-in-aid are given by the federal government<br />
for two major reasons: political (e.g. to aid the taking off of a state or local government)<br />
and to reduce the effect of unforeseen occurrences (like flood/rainstorm, draught, pest<br />
problem, crisis, etc.) that can distort the budget of the unit concerned to the extent that<br />
other essential services could suffer. With regards to VAT, introduced in 1994, the<br />
sharing is at 15%, 50% and 35% among the federal, state and local governments<br />
respectively (Seyi Ojo, 1999:178) (as quoted by Adesopo, et. al., 2004:186). The<br />
horizontal sharing of VAT proceeds among each lower level of government is on the<br />
basis of equality (50%), population (30%) and derivation (20%). Lastly, education tax is<br />
a peculiar (centrally collected) revenue. It is peculiar first because it is specially<br />
managed by a Board of Trustee and second, it is not directly shared among the tiers of<br />
government. Despite this, it indirectly benefits the three tiers of government as it is spent<br />
to develop education at all levels. As an amendment to the disbursement ratio, effective<br />
from 1998, the disbursement has been among Higher education (50%), secondary<br />
education (20%) and primary education (30%) irrespective of the tier of government that<br />
owns the institution. This was initially (in 1993) in ratio 50:10:40 respectively.<br />
Highlighting sources of fiscal stress at local government level<br />
With respect to the above listed issues, we shall be concerning ourselves with the sources<br />
of fiscal stress at the local government level. By the way, fiscal stress is a fiscal situation<br />
that can be equated to budgetary stringency. It is the next stage to financial insolvency<br />
and/or fiscal crisis when expenditure is related to revenue. When revenue and<br />
expenditure run neck to neck, there exists a state of fiscal stress and when this situation is<br />
not checked what results is a higher level of fiscal dislocation better known as fiscal<br />
54