89-91 - Polskie Stowarzyszenie Biomateriałów
89-91 - Polskie Stowarzyszenie Biomateriałów
89-91 - Polskie Stowarzyszenie Biomateriałów
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
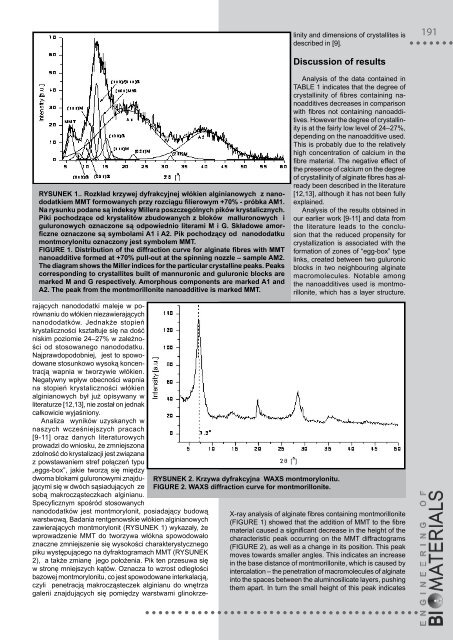
ysunek 1.. rozkład krzywej dyfrakcyjnej włókien alginianowych z nanododatkiem<br />
mmt formowanych przy rozciągu filierowym +70% - próbka am1.<br />
na rysunku podane są indeksy millera poszczególnych pików krystalicznych.<br />
piki pochodzące od krystalitów zbudowanych z bloków malluronowych i<br />
guluronowych oznaczone są odpowiednio literami m i g. składowe amorficzne<br />
oznaczone są symbolami a1 i a2. pik pochodzący od nanododatku<br />
montmorylonitu oznaczony jest symbolem mmt.<br />
figure 1. distribution of the diffraction curve for alginate fibres with mmt<br />
nanoadditive formed at +70% pull-out at the spinning nozzle – sample am2.<br />
the diagram shows the miller indices for the particular crystalline peaks. peaks<br />
corresponding to crystallites built of mannuronic and guluronic blocks are<br />
marked m and g respectively. amorphous components are marked a1 and<br />
a2. the peak from the montmorillonite nanoadditive is marked mmt.<br />
rających nanododatki maleje w porównaniu<br />
do włókien niezawierających<br />
nanododatków. Jednakże stopień<br />
krystaliczności kształtuje się na dość<br />
niskim poziomie 24–27% w zależności<br />
od stosowanego nanododatku.<br />
Najprawdopodobniej, jest to spowodowane<br />
stosunkowo wysoką koncentracją<br />
wapnia w tworzywie włókien.<br />
Negatywny wpływ obecności wapnia<br />
na stopień krystaliczności włókien<br />
alginianowych był już opisywany w<br />
literaturze [12,13], nie został on jednak<br />
całkowicie wyjaśniony.<br />
Analiza wyników uzyskanych w<br />
naszych wcześniejszych pracach<br />
[9-11] oraz danych literaturowych<br />
prowadzi do wniosku, że zmniejszona<br />
zdolność do krystalizacji jest związana<br />
z powstawaniem stref połączeń typu<br />
„eggs-box”, jakie tworzą się między<br />
dwoma blokami guluronowymi znajdującymi<br />
się w dwóch sąsiadujących ze<br />
sobą makrocząsteczkach alginianu.<br />
Specyficznym spośród stosowanych<br />
nanododatków jest montmorylonit, posiadający budową<br />
warstwową. Badania rentgenowskie włókien alginianowych<br />
zawierających montmorylonit (rySuNEk 1) wykazały, że<br />
wprowadzenie MMT do tworzywa włókna spowodowało<br />
znaczne zmniejszenie się wysokości charakterystycznego<br />
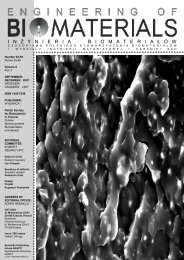
piku występującego na dyfraktogramach MMT (rySuNEk<br />
2), a także zmianę jego położenia. Pik ten przesuwa się<br />
w stronę mniejszych kątów. Oznacza to wzrost odległości<br />
bazowej montmorylonitu, co jest spowodowane interkalacją,<br />
czyli penetracją makrocząsteczek alginianu do wnętrza<br />
galerii znajdujących się pomiędzy warstwami glinokrze-<br />
linity and dimensions of crystallites is<br />
described in [9].<br />
discussion of results<br />
rysunek 2. krzywa dyfrakcyjna waXs montmorylonitu.<br />
figure 2. waXs diffraction curve for montmorillonite.<br />
Analysis of the data contained in<br />
TABLE 1 indicates that the degree of<br />
crystallinity of fibres containing nanoadditives<br />
decreases in comparison<br />
with fibres not containing nanoadditives.<br />
however the degree of crystallinity<br />
is at the fairly low level of 24–27%,<br />
depending on the nanoadditive used.<br />
This is probably due to the relatively<br />
high concentration of calcium in the<br />
fibre material. The negative effect of<br />
the presence of calcium on the degree<br />
of crystallinity of alginate fibres has already<br />
been described in the literature<br />
[12,13], although it has not been fully<br />
explained.<br />
Analysis of the results obtained in<br />
our earlier work [9-11] and data from<br />
the literature leads to the conclusion<br />
that the reduced propensity for<br />
crystallization is associated with the<br />
formation of zones of “egg-box” type<br />
links, created between two guluronic<br />
blocks in two neighbouring alginate<br />
macromolecules. Notable among<br />
the nanoadditives used is montmorillonite,<br />
which has a layer structure.<br />
X-ray analysis of alginate fibres containing montmorillonite<br />
(FIGurE 1) showed that the addition of MMT to the fibre<br />
material caused a significant decrease in the height of the<br />
characteristic peak occurring on the MMT diffractograms<br />
(FIGurE 2), as well as a change in its position. This peak<br />
moves towards smaller angles. This indicates an increase<br />
in the base distance of montmorillonite, which is caused by<br />
intercalation – the penetration of macromolecules of alginate<br />
into the spaces between the aluminosilicate layers, pushing<br />
them apart. In turn the small height of this peak indicates<br />
1<strong>91</strong>