2006 - Institut für Klinische Chemie - UniversitätsSpital Zürich
2006 - Institut für Klinische Chemie - UniversitätsSpital Zürich
2006 - Institut für Klinische Chemie - UniversitätsSpital Zürich
Erfolgreiche ePaper selbst erstellen
Machen Sie aus Ihren PDF Publikationen ein blätterbares Flipbook mit unserer einzigartigen Google optimierten e-Paper Software.
Universität <strong>Zürich</strong> > Medizinische Fakultät > <strong>Klinische</strong> <strong>Chemie</strong>, <strong>Institut</strong> <strong>für</strong> > Prof. Dr.<br />
Arnold von Eckardstein<br />
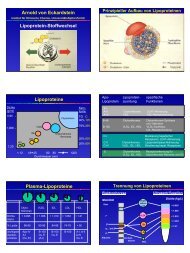
Atherosclerosis and Genetics of the Lipoxygenase Pathways<br />
Summary / Zusammenfassung<br />
Atherosclerosis is the pathogenetic process leading to myocardial infarction and stroke and still is<br />
the leading cause of death in Western civilisation. Chronic inflammation plays a major role in<br />
atherogenesis and understanding the role of inflammation and its resolution will offer novel<br />
approaches to interfere with atherogenesis. The lipoxygenase pathway plays a role in inflammation<br />
and in its resolution and functional polymorphisms in these genes will eventually alter the balance<br />
between pro- and anti-inflammation. We screen these genes for polymorphisms in the Caucasian<br />
population, investigate the functionality of such newly discovered polymorphisms in cell culture<br />
and investigate their association with atherosclerosis in patients with coronary artery disease. Such<br />
an approach allows studying the pro- or anti-atherogenic role of a certain enzyme independent of<br />
exogenous factors and in vitro conditions.<br />
Publications / Publikationen<br />
J. Wittwer, M. Bayer, A. Mosandl, J. Muntwyler and M. Hersberger. The c.-292C>T promoter<br />
polymorphism increases ALOX15 activity and could be atheroprotective. In press Clin Chem Lab<br />
Med 2007.<br />
J. Wittwer, J. Marti-Jaun and M. Hersberger. A Functional Polymorphism in ALOX15 Results in<br />
Increased Allele-Specific Transcription in Macrophages Through Binding of the Transcription<br />
Factor SPI1. Hum Mutat. <strong>2006</strong> Jan;27(1):78-87.<br />
J. Muntwyler, J. Marti-Jaun, TF. Lüscher, E. Hänseler and M. Hersberger. The Asp298 but not the<br />
C-786 genotype of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase is reduced with age in healthy Swiss men.<br />
Clin Chem Lab Med 2005;43(9):971–973<br />
M. Hersberger, J. Muntwyler, H. Funke, J. Marti-Jaun, H. Schulte, G. Assmann, TF. Lüscher and<br />
A von Eckardstein. Association of the CAG Repeat Polymorphism in the Androgen Receptor with<br />
HDL Cholesterol but not with Coronary Atherosclerosis or Myocardial Infarction. Clin Chem<br />
2005; 51: 1110-1115.<br />
J. Muntwyler, J. Marti-Jaun, T.F. Lüscher, E. Hänseler and M. Hersberger. No evidence for an<br />
involvement of the human inducible nitric oxide synthase gene in susceptibility to coronary artery<br />
disease. Clin Chem Lab Med 2005;43(2):253-255.<br />
Keywords / Suchbegriffe<br />
Atherosclerosis, lipoxygenases, risk factors, gene regulation, genetics, polymorphisms<br />
Project Leadership and Contacts / Projektleitung und Kontakte<br />
PD Dr. Martin Hersberger (Project Leader) hmr@ikc.uzh.ch<br />
Funding Source(s) / Unterstützt durch<br />
SNF (Personen- und Projektförderung)<br />
OPO Stiftung, Olga Mayenfisch Stiftung<br />
Project 6198<br />
Seite 1<br />
All