2006 - Institut für Klinische Chemie - UniversitätsSpital Zürich
2006 - Institut für Klinische Chemie - UniversitätsSpital Zürich
2006 - Institut für Klinische Chemie - UniversitätsSpital Zürich
Sie wollen auch ein ePaper? Erhöhen Sie die Reichweite Ihrer Titel.
YUMPU macht aus Druck-PDFs automatisch weboptimierte ePaper, die Google liebt.
Universität <strong>Zürich</strong> > Medizinische Fakultät > <strong>Klinische</strong> <strong>Chemie</strong>, <strong>Institut</strong> <strong>für</strong> > Prof. Dr.<br />
Arnold von Eckardstein<br />
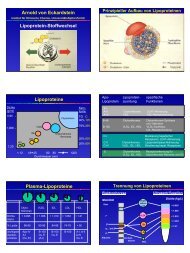
High density lipoproteins (HDL) and arteriosclerosis<br />
Original title / Originaltitel<br />
High density lipoproteins (HDL), cellular lipid metabolism and arteriosclerosis<br />
Summary / Zusammenfassung<br />
Plasma levels of HDL and its major protein component, apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I), are inversely<br />
correlated with the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. ApoA-I and HDL may be<br />
atheroprotective because they promote the reverse transport of cholesterol from macrophages of<br />
the arterial wall to the liver. Within the arterial wall, this process requires interactions of apoA-I or<br />
HDL with endothelial cells for entering the subendothelial space and with macrophages for<br />
mediating cholesterol efflux. As for all plasma proteins, it is controversial whether apoA-I is<br />
unspecifically filtrated or transcytosed via a receptor/transporter mediated pathway through the<br />
endothelium. It is also controversial whether cholesterol efflux from macrophages is a pure cell<br />
surface event or whether it involves uptake and resecretion of apoA-I or HDL (so-called<br />
retroendocytosis). Supported by a grant from the Swiss National Foundation we therefore<br />
characterize the binding, internalization and resecretion of HDL and apoA-I by endothelial cells<br />
and macrophages. Our data suggest that receptor-dependent interactions of apoA-I with endothelial<br />
cells and macrophages leads to transcytosis and retroendocytosis, respectively. We are in the<br />
process of characterizing these receptors. The understanding of this process may unravel novel<br />
targets for anti-atherosclerotic drug therapy but also help to develop novel strategies for drug<br />
delivery, either into the arterial wall or in general into extravascular compartments, e.g. through<br />
the blood-brain-barrier.<br />
Publications / Publikationen<br />
Rohrer L, Cavelier C, Fuchs S, Schlüter MA, Völker W, von Eckardstein A (<strong>2006</strong>). Binding,<br />
Internalization and Transport of Apolipoprotein A-I by Vascular Endothelial Cells. Biochim.<br />
Biophys Acta Mol. Cell. Biol. Lipids 1761, 186-194<br />
Nofer JR, Remaley AT, Feuerborn R, Wolinska I, Engel T, von Eckardstein A, Assmann G (<strong>2006</strong>).<br />
Apolipoprotein A-I (APO A-I) activates CDC42 signaling through ABCA1 transporter. J. Lipid<br />
Res. 47:794-803<br />
Cavelier C, Rohrer L, von Eckardstein A (<strong>2006</strong>). ABCA1 Modulates ApoA-I Transcytosis<br />
Through Aortic Endothelial Cells. Circulation Research, 99(10):1060-6.<br />
Cavelier C, Lorenzi I, Rohrer L, von Eckardstein A (<strong>2006</strong>). Lipid Efflux by the ATP Binding<br />
Cassette Transporters ABCA1 and ABCG1. Biochim Biophys Acta. Mol. Cell. Biol. Lipids <strong>2006</strong>,<br />
1761(7):655-66<br />
Keywords / Suchbegriffe<br />
HDL, atherosclerosis, ABCA1, lipid metabolism, macrophages, endothelial cells<br />
Project Leadership and Contacts / Projektleitung und Kontakte<br />
Prof. Dr. Arnold von Eckardstein (Project Leader) arnold.voneckardstein@ikc.usz.ch<br />
Dr. Lucia Rohrer (Project Leader) lucia.rohrer@ikc.usz.ch<br />
Project 2733<br />
Seite 1<br />
All