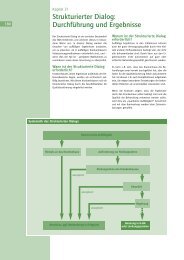
Ambulant erworbene Pneumonie
Ambulant erworbene Pneumonie
Ambulant erworbene Pneumonie
Sie wollen auch ein ePaper? Erhöhen Sie die Reichweite Ihrer Titel.
YUMPU macht aus Druck-PDFs automatisch weboptimierte ePaper, die Google liebt.
<strong>Ambulant</strong> <strong>erworbene</strong> <strong>Pneumonie</strong><br />
Menéndez R, Torres A, Zalacaín R, Aspa J, Martín<br />
Villasclaras JJ, Borderías L, Benítez Moya JM,<br />
Ruiz-Manzano J, Rodríguez de Castro F, Blanquer J,<br />
Pérez D, Puzo C, Sánchez Gascón, Gallardo J,<br />
Álvarez C, Molinos L (Neumofail Group).<br />
Risk Factors of treatment failure in community<br />
acquired pneumonia: implications for disease<br />
outcome.<br />
Thorax 2004; 59: 960-965.<br />
NGC National Guideline Clearinghouse.<br />
Evidence-based guidelines for weaning and discontinuation<br />
of ventilatory support.<br />
Chest 2001; 120: 375-484.<br />
SIGN Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network.<br />
Community Management of Lower Respiratory Tract<br />
Infection in Adults – A national clinical guideline.<br />
Section 5. Community Acquired Pneumonia 2002.<br />
http://www.sign.ac.uk/guidelines/fulltext/59/<br />
section5.html (Recherchedatum: 13.06.2006).<br />
Welte T, Marre R, Suttorp N.<br />
CAPNETZ – Kompetenznetzwerk ambulant<br />
<strong>erworbene</strong> <strong>Pneumonie</strong>: Strukturen und Ziele.<br />
Pneumologie 2003; 57: 34-41.