Spiegelberg:Sonde 2 Gebrauchsinformation. Sorgfältig lesen!
Spiegelberg:Sonde 2 Gebrauchsinformation. Sorgfältig lesen!
Spiegelberg:Sonde 2 Gebrauchsinformation. Sorgfältig lesen!
Sie wollen auch ein ePaper? Erhöhen Sie die Reichweite Ihrer Titel.
YUMPU macht aus Druck-PDFs automatisch weboptimierte ePaper, die Google liebt.
<strong>Spiegelberg</strong>: <strong>Sonde</strong> 2<br />
<strong>Gebrauchsinformation</strong>. <strong>Sorgfältig</strong> <strong>lesen</strong>!<br />
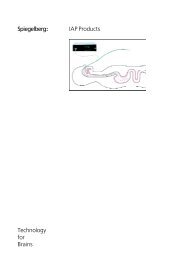
Methode<br />
Das Luftkammer-System ist ein Hohlkörper<br />
aus Kunststoff, der über einen<br />
Schlauch mit einem Druckaufnehmer<br />
verbunden ist. Der Druckaufnehmer befindet<br />
sich zusammen mit der Meßelektronik<br />
und einer Vorrichtung zur Füllung<br />
der Luftkammer in dem Hirndruck-<br />
Meßgerät.<br />
Zur epiduralen Druckmessung wird die<br />
Luftkammer auf der Dura des Patienten<br />
plaziert. Der intrakranielle Druck wird<br />
über die dünne Wand der Luftkammer<br />
auf die Luft in der Kammer übertragen<br />
und vom Druckaufnehmer in elektrische<br />
Signale umgesetzt.<br />
Auf dem Display des Gerätes werden<br />
der Mitteldruck und während der ersten<br />
zehn Minuten nach dem Einschalten<br />
auch die Pulsamplitude angezeigt.<br />
Am Monitorausgang stehen sowohl der<br />
Mitteldruck als auch das pulsatile Signal<br />
zur Verfügung.<br />
Das Hirndruck-Meßgerät öffnet den<br />
Druckaufnehmer einmal pro Stunde zur<br />
Atmosphäre und stellt den Nullpunkt<br />
ein. Danach wird die Luftkammer mit<br />
dem Volumen gefüllt, das für die Druckübertragung<br />
erforderlich ist.<br />
Indikation und Technik<br />
Am besten geeignet ist die <strong>Sonde</strong> 2 für<br />
die Druckmessung nach großer<br />
Trepanation.<br />
Soll der Luftschlauch subgaleal ausgeleitet<br />
werden, ist eine Hautinzision<br />
von ca. 1 cm Länge erforderlich. Der<br />
<strong>Sonde</strong>nkopf muß dann von außen nach<br />
innen geführt werden. Dies gelingt relativ<br />
leicht wenn man zunächst eine<br />
Schlaufe des Luftschlauches einschiebt<br />
und dann die <strong>Sonde</strong> nachzieht. Das<br />
Fassen und Vorschieben der <strong>Sonde</strong><br />
z. B. mit einer Pinzette sollte wegen<br />
der möglichen Perforation nicht erfolgen.<br />
Grundsätzlich möglich ist die Applikation<br />
über ein Bohrloch nach ausreichender<br />
Ablösung der Dura. Hierbei besteht<br />
allerdings die erhöhte Gefahr einer<br />
epiduralen Blutung.<br />
Überprüfen der <strong>Sonde</strong><br />
<strong>Sonde</strong> am Hirndruck-Meßgerät<br />
konnektieren. Das Schlauchende und<br />
der Konnektor werden dabei unsteril.<br />
Gerät einschalten und Entleerung und<br />
Füllung der Luftkammer beobachten.<br />
Die Druckanzeige muß bei etwa 0<br />
mmHg stehen. Die restliche Prüfung erfolgt<br />
mit dem palpierenden Finger<br />
(feucht). Leichten, pulsierenden Druck<br />
auf die Luftkammer ausüben. Am Monitor<br />
Pulsation beobachten.<br />
Mögliche Fehlerquellen sind:<br />
Adhärenzen der Meßmembran, dadurch<br />
artifizieller Druck. Solche<br />
Adhärenzen können durch Manipulationen<br />
an der Membran gelöst werden.<br />
Undichtigkeit der <strong>Sonde</strong>, rote Warnanzeige<br />
blinkt, <strong>Sonde</strong> muß ausgetauscht<br />
werden.<br />
Plazieren der <strong>Sonde</strong> 2<br />
Die <strong>Sonde</strong> wird durch eines der vorhandenen<br />
Bohrlöcher in gerader Richtung<br />
so unter den Knochendeckel geführt,<br />
daß die Meßmembran auf der<br />
Dura liegt. Cave: Perforation an<br />
Knochenkanten. Eventuelle<br />
Durahochnähte müssen weit genug<br />
entfernt sein.<br />
<strong>Sonde</strong> am Hirndruck-Meßgerät<br />
konnektieren, Gerät einschalten, Hirndruck<br />
messen. Möglichst am Monitor<br />
Pulsation beobachten. Die Amplitude<br />
des Hirndruckpulses sollte in plausiblem<br />
Verhältnis zum mittleren Hirndruck<br />
stehen. Beim Gesunden hat die<br />
ICP-Welle eine Amplitude von 1-4<br />
mmHg. Sie steigt bei Drucksteigerungen<br />
auf 10-20 mmHg und mehr an.<br />
Wenn der gemessene ICP bei niedriger<br />
Amplitude zu hoch erscheint, können<br />
ungenügende Duraablösung, ein abgeknickter<br />
Schlauch oder verkippte<br />
Lage der <strong>Sonde</strong> im Bohrloch dafür verantwortlich<br />
sein.<br />
Je nach Situation den ICP bis zu zehn<br />
Minuten messen. Bei deutlichem<br />
Druckanstieg ohne gleichzeitigen Anstieg<br />
der Amplitude kann eine<br />
epidurale Blutung vorliegen. Dann<br />
<strong>Sonde</strong> revidieren und erneut Druckverlauf<br />
abwarten.<br />
0297<br />
SND13.1.12/FV531P<br />
Entfernung der <strong>Sonde</strong> 2<br />
Nach Dekonnektion vom Hirndruck-Meßgerät<br />
und nach Lösen einer eventuellen<br />
Adaptationsnaht an der Austrittsinzision<br />
kann die <strong>Sonde</strong> 2 am Luftschlauch aus der<br />
Wunde gezogen werden. Eventuell<br />
Sekundärnaht.<br />
Warnung<br />
Diese <strong>Sonde</strong> ist zur einmaligen Verwendung<br />
zur Hirndruckmessung mit dem<br />
<strong>Spiegelberg</strong> Monitor HDM 13.x, HDM 26.x<br />
oder HDM 29.x bestimmt. Nicht<br />
resterilisieren. Nicht wiederverwenden.<br />
Bei Wiederverwendung besteht ein<br />
Infektionsrisiko. Niemals Kochsalzlösung<br />
oder ein anderes flüssiges Medium einfüllen.<br />
Nicht verwenden wenn Packung beschädigt.<br />
Technische Daten<br />
Bestell Nr. SND13.1.12/FV531P<br />
Material Pellethane<br />
Füllvolumen 0,05 - 0,1 ml<br />
Außendurchmesser 2 mm<br />
Länge 1500 mm<br />
Anwendungsdauer kurzzeitig<br />
bis zu 30 Tagen<br />
Doppelt verpackt<br />
EO sterilisiert<br />
Zur einmaligen Verwendung<br />
Hersteller<br />
<strong>Spiegelberg</strong><br />
GmbH & Co. KG<br />
Tempowerkring 4<br />
21079 Hamburg<br />
Germany<br />
Telefon: 040-790-178-0<br />
Telefax: 040-790-178-10<br />
Email: Info@<strong>Spiegelberg</strong>.de<br />
Version: 7.1 / 2013-05-31
<strong>Spiegelberg</strong>: Probe 2<br />
Directions for use. Read carefully!<br />
Method<br />
The air-pouch system consists of a<br />
hollow body connected to a pressure<br />
transducer by tubing. The pressure<br />
transducer, the electronic hardware,<br />
and the device for filling the air-pouch<br />
are integrated in the Brain-Pressure<br />
Monitor.<br />
For epidural pressure measurement the<br />
air- pouch is placed on the dura of the<br />
patient. The intracranial pressure is<br />
transmitted across the thin pouch wall<br />
to the air volume in the pouch and<br />
transformed into an electric signal by<br />
the pressure transducer.<br />
On the digital display the mean<br />
pressure is shown. At the monitor<br />
output both the mean pressure and<br />
the pulsatile signal are available.<br />
Once every hour the Brain-Pressure<br />
Monitor opens the pressure transducer<br />
to atmospheric pressure for zero<br />
adjustment. The air-pouch is then filled<br />
with the exact air volume required for<br />
accurate pressure transmission.<br />
Indication and Function<br />
Probe 2 is to be used postoperatively<br />
after large trepanation. If the air-tube<br />
is to be placed in a subgaleal tunnel a<br />
skin incision of about 1 cm in length is<br />
necessary. The probe head is then<br />
introduced in a distal to proximal<br />
direction. This is done fairly easily by<br />
forming a loop of the tubing and<br />
pushing the loop through the tunnel.<br />
The probe head is then pulled through<br />
the tunnel. Due to the risk of<br />
perforating the diaphragm the probe<br />
head should not be handed with a<br />
forceps or other sharp tool.<br />
In principle, after mobilisation of a<br />
sufficiently large area of the dura, the<br />
probe can be inserted between the<br />
dura and the cranial bone through a<br />
burr-hole. This application has a higher<br />
risk of epidural hematoma.<br />
Probe Check<br />
Connect probe to Brain-Pressure Monitor.<br />
Note that the tube end and the<br />
connector are non-sterile now. Switch<br />
on monitor and watch emptying and<br />
filling of air-pouch. The pressure<br />
reading must be around zero.<br />
Remaining checks with palpating<br />
finger (moist). Apply a slightly pulsating<br />
pressure on the air-pouch. Watch the<br />
undulating signal on the monitor.<br />
Possible sources of error are:<br />
Pressure artifacts caused by adherence<br />
of probe membrane. Resolve by<br />
manipulating membrane.<br />
Leaky probe, red warning indicator<br />
appears. Probe should be replaced.<br />
No pulsation on the monitor. Tubing<br />
kinked or clogged. 0297<br />
Placement of Probe 2<br />
The probe is placed under the bone<br />
flap such that the measuring<br />
diaphragm is in contact with the dura.<br />
A perforation of the diaphragm at the<br />
bone edge is to be avoided. The probe<br />
is to be placed away from possible<br />
sutures of the dura.<br />
Connect probe to Brain-Pressure Monitor,<br />
switch on monitor, read brain<br />
pressure. It is advised to check for<br />
pulsation on a patient monitor. The<br />
amplitude of the brain-pressure should<br />
be plausible in relation to the mean<br />
pressure. In healthy man the ICP-wave<br />
has an amplitude of 1 to 4 mmHg. With<br />
elevated ICP the amplitude rises to 10-<br />
20 mmHg and even more. If the<br />
measured ICP appears to be high with<br />
a low amplitude, the dura might not be<br />
stripped from the bone sufficiently. Also<br />
a kinked tubing or a tilted probe could<br />
be the cause. Depending on the<br />
situation continue to read the ICP for<br />
up to 10 minutes. A distinct rise of the<br />
mean ICP which is not accompanied by<br />
a rise of the amplitude can indicate an<br />
epidural hematoma. In that case<br />
remove the hematoma and read ICP<br />
anew.<br />
Direct air tube vertically out of wound,<br />
close with approximately four<br />
interrupted sutures. Affix suture flap,<br />
form loop.<br />
SND13.1.12/FV531P<br />
Removal of Probe 2<br />
Disconnect probe from the Brain-Pressure<br />
Monitor. After loosening of a possible<br />
suture at the skin incision Probe 2 is<br />
pulled out of the wound. Possibly<br />
secondary suture.<br />
Warning<br />
This probe is designed and is intended for<br />
single use for the measurement of ICP with<br />
the <strong>Spiegelberg</strong> Monitor HDM 13.x, HDM<br />
26.x, or HDM 29.x. Do not resterilize. Do<br />
not reuse. With reuse an infection risk<br />
exists. Do not fill with saline or other liquid<br />
media. Do not use if package is damaged.<br />
Technical Information<br />
Order No. SND13.1.12/FV531P<br />
Material Pellethane<br />
Filling volume 0,05 - 0,1 ml<br />
Outer diameter 2 mm<br />
Length 1500 mm<br />
Duration of use short term<br />
not more than 30 days<br />
Double packed<br />
EO sterilized<br />
For single use<br />
Manufacturer<br />
<strong>Spiegelberg</strong><br />
GmbH & Co. KG<br />
Tempowerkring 4<br />
21079 Hamburg<br />
Germany<br />
Phone: +49-40-790-178-0<br />
Fax: +49-40-790-178-10<br />
Email: Info@<strong>Spiegelberg</strong>.de<br />
Version: 7.1 / 2013-05-31